Students are completing a table about a particular subatomic – As students embark on the task of completing a comprehensive table on a particular subatomic particle, they delve into the fascinating realm of physics, uncovering the fundamental building blocks of matter. This table serves as a valuable tool for understanding the properties and behaviors of these particles, providing a deeper insight into the very fabric of our universe.
The subatomic particle(s) under investigation in this table play a crucial role in shaping the world around us. By examining their characteristics, students gain a deeper understanding of atomic structure, chemical reactions, and the forces that govern the interactions between matter and energy.
Student Understanding: Students Are Completing A Table About A Particular Subatomic
The table students are completing serves as a comprehensive record of essential information about specific subatomic particles. Its primary purpose is to enhance students’ understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter and their properties. By completing this table, students will develop a deeper grasp of the structure and behavior of atoms, fostering a solid foundation for further studies in chemistry and physics.
Subatomic Particles in Focus, Students are completing a table about a particular subatomic
The table focuses on three key subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, while neutrons are neutral particles also located in the nucleus. Electrons, on the other hand, are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels.
Significance of Particle Properties
Understanding the properties and behavior of these subatomic particles is crucial for comprehending the chemical and physical properties of elements and compounds. Protons determine an atom’s atomic number and its chemical identity, while neutrons contribute to its mass and stability.
Electrons govern the atom’s chemical reactivity and participate in the formation of chemical bonds.
Table Structure
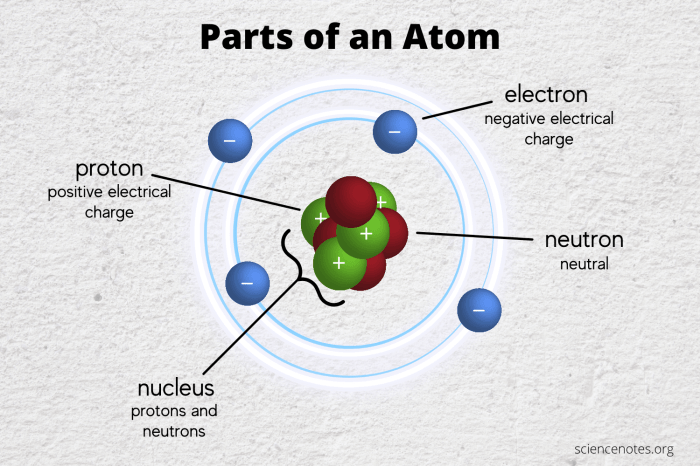
The table consists of three main columns, each dedicated to a specific subatomic particle: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each column is further divided into subcolumns that provide specific information about the particle’s charge, mass, location, and other relevant properties.
Column Headings and Significance
- Particle:Indicates the type of subatomic particle being described.
- Charge:Specifies the electrical charge of the particle, either positive, negative, or neutral.
- Mass:Provides the mass of the particle, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
- Location:Describes the particle’s location within the atom, whether it is found in the nucleus or in an electron orbital.
- Other Properties:Includes additional information about the particle’s behavior or characteristics, such as its spin or magnetic properties.
Formatting and Conventions
The table follows a consistent formatting style, using clear and concise language. Numerical values are presented with appropriate units, and particle symbols are used to represent the subatomic particles.
Data Collection and Analysis
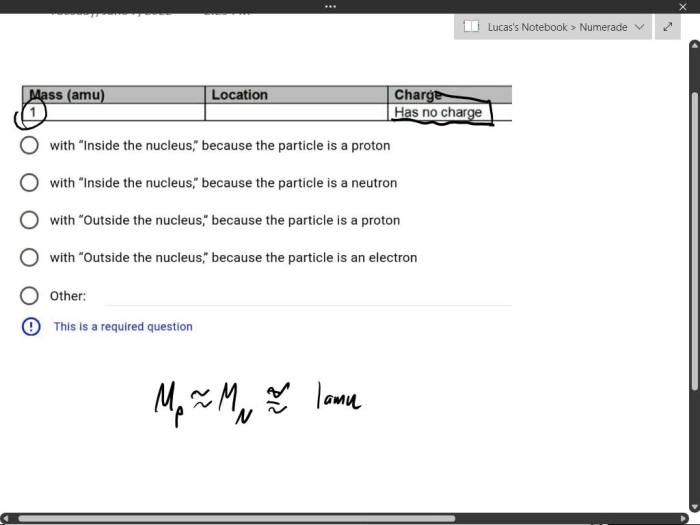
Students should gather data for the table from reliable sources, such as textbooks, scientific journals, or online databases. It is essential to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the information.
Data Analysis Techniques
- Pattern Identification:Students should analyze the data to identify patterns and relationships between the different properties of the subatomic particles.
- Comparison and Contrast:Students should compare and contrast the properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons to highlight their similarities and differences.
- Drawing Conclusions:Based on the analysis, students should draw conclusions about the behavior and interactions of these particles within atoms.
Interpretation and Presentation
Students should interpret the results of their analysis and present them clearly and concisely in the table. They should use appropriate units and symbols to convey the information accurately.
Table Applications
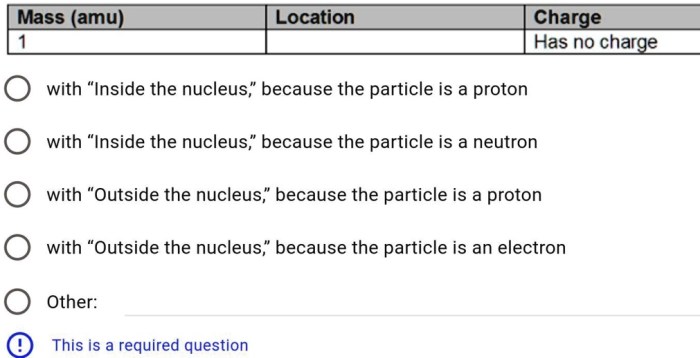
The completed table can serve as a valuable resource for students as they continue their studies in chemistry and physics. It provides a quick and easy reference for the properties of subatomic particles.
Further Learning Support
- Reinforcement of Concepts:The table helps reinforce students’ understanding of the fundamental concepts of atomic structure.
- Problem Solving:Students can use the table to solve problems related to atomic mass, charge, and other particle properties.
- Prediction and Analysis:The table enables students to make predictions and analyze the behavior of atoms based on the properties of their subatomic particles.
Real-World Applications
- Nuclear Physics:The table is essential for understanding nuclear reactions and the properties of radioactive isotopes.
- Materials Science:The properties of subatomic particles influence the behavior and properties of materials.
- Quantum Mechanics:The table provides a foundation for understanding the quantum mechanical behavior of electrons.
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of the table students are completing?
The table helps students organize and analyze data on a specific subatomic particle, providing a comprehensive overview of its properties and behaviors.
How do students gather data for the table?
Students can use various methods to collect data, including textbooks, scientific articles, online resources, and experiments.
What is the significance of understanding the properties of subatomic particles?
Understanding the properties of subatomic particles is essential for comprehending the structure and behavior of matter, as well as the fundamental forces that govern the universe.