Embark on a comprehensive journey into the realm of Ceretec white blood cell scans, where we unravel the intricacies of this diagnostic tool, its clinical applications, and its impact on patient care. Brace yourself for an enlightening exploration that seamlessly blends scientific precision with an engaging narrative.
As we delve into the depths of this topic, we’ll uncover the purpose and procedure of Ceretec scans, their indications and interpretation, their advantages and limitations, and their invaluable role in clinical practice. Along the way, we’ll delve into real-world examples and answer frequently asked questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of this essential diagnostic tool.
Ceretec White Blood Cell Scan Overview
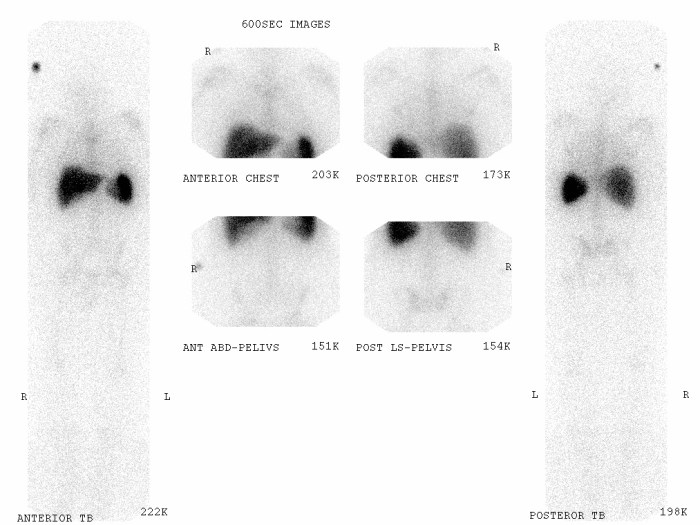
A Ceretec white blood cell scan is a medical imaging procedure used to detect and evaluate infections or inflammation in the body. It involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, which then travels throughout the body and accumulates in areas with high concentrations of white blood cells, such as sites of infection or inflammation.
Procedure, Ceretec white blood cell scan
Undergoing a Ceretec white blood cell scan typically involves the following steps:
- The patient is injected with the radioactive tracer through a vein in the arm.
- The patient waits for several hours to allow the tracer to circulate and accumulate in the target areas.
- The patient undergoes a scan using a special camera that detects the radioactive emissions from the tracer.
- The images obtained from the scan are analyzed by a doctor to identify areas of infection or inflammation.
Indications for a Ceretec White Blood Cell Scan
A Ceretec white blood cell scan is a nuclear medicine imaging test that helps diagnose and evaluate various medical conditions related to inflammation and infection. It involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, which is then absorbed by white blood cells and carried to areas of infection or inflammation.
The Ceretec white blood cell scan is a valuable tool for diagnosing infections and inflammation. While this technique is widely used in medical settings, it’s also worth noting that a chemist burns 160.0 g of al in a separate experiment.
Despite their differences, both procedures demonstrate the versatility of scientific methods in addressing diverse challenges. Returning to the Ceretec scan, its ability to detect even small amounts of infection makes it a crucial diagnostic tool in modern medicine.
Common medical conditions or situations where a Ceretec white blood cell scan is indicated include:
- Suspected infection:To locate and identify the source of an infection, such as in cases of fever of unknown origin, osteomyelitis (bone infection), or suspected abscesses.
- Evaluation of inflammatory conditions:To assess the extent and severity of inflammatory processes, such as in cases of vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), inflammatory bowel disease, or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Monitoring response to treatment:To track the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy or other treatments for infections or inflammatory conditions.
- Preoperative planning:To guide surgical interventions by identifying the precise location of an infection or inflammation, aiding in surgical planning and minimizing the risk of complications.
- Assessment of prosthetic joint infection:To diagnose and differentiate between infection and aseptic loosening of a prosthetic joint.
Interpretation of Ceretec White Blood Cell Scan Results
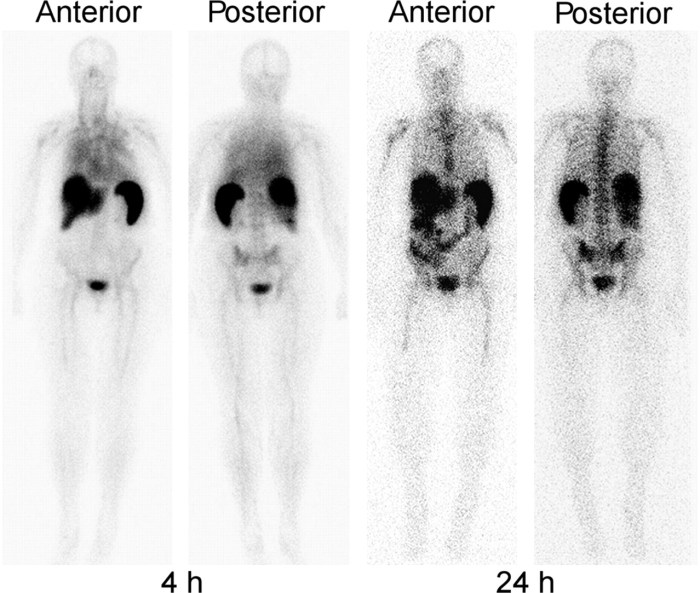
Ceretec white blood cell scans are interpreted by comparing the distribution and intensity of the radioactive tracer in the body to established normal patterns. Deviations from these patterns may indicate the presence of infection or inflammation.
Normal Findings
In a normal Ceretec white blood cell scan, the tracer is distributed evenly throughout the body, with no areas of increased or decreased activity. The spleen, liver, and bone marrow may show slightly higher uptake of the tracer, as these are sites of normal white blood cell production and storage.
Abnormal Findings
Abnormal findings on a Ceretec white blood cell scan may include:
- Areas of increased tracer uptake: This may indicate the presence of infection or inflammation in the affected area. For example, an increased uptake in the lungs may suggest pneumonia, while increased uptake in the abdomen may indicate appendicitis.
- Areas of decreased tracer uptake: This may indicate a lack of blood flow to the affected area, which can be caused by a variety of conditions such as blood clots or vascular disease.
- Abnormal distribution of tracer: This may indicate a problem with the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining fluid and waste products from the body.
Specific Medical Conditions
Ceretec white blood cell scans can be used to detect or rule out a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Infection: Ceretec scans can help diagnose infections in various parts of the body, such as pneumonia, appendicitis, and osteomyelitis (bone infection).
- Inflammation: Ceretec scans can help detect inflammation in organs such as the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
- Abscesses: Ceretec scans can help locate and diagnose abscesses, which are collections of pus that can form in various parts of the body.
- Vascular disease: Ceretec scans can help detect blood clots and other vascular problems that can affect blood flow to different parts of the body.
Advantages and Limitations of a Ceretec White Blood Cell Scan
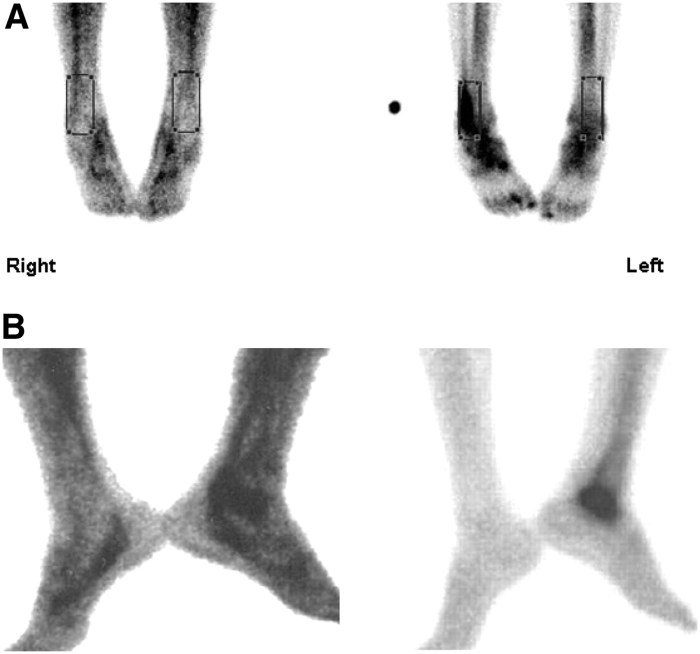
A Ceretec white blood cell scan is a nuclear medicine imaging test that uses a radioactive tracer to visualize and evaluate the distribution and activity of white blood cells in the body. Compared to other diagnostic tests, a Ceretec white blood cell scan offers several advantages:
- Non-invasive:Unlike invasive procedures like biopsies, a Ceretec scan is non-invasive, involving only an injection of the radioactive tracer and subsequent imaging.
- Whole-body imaging:It provides a comprehensive view of white blood cell activity throughout the body, making it useful for detecting widespread infections or inflammatory conditions.
- High sensitivity:Ceretec scans have high sensitivity, meaning they can detect even small amounts of white blood cell activity, increasing the likelihood of identifying infections or inflammation.
However, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Limited specificity:Ceretec scans can sometimes produce false-positive results, as they may detect non-infectious inflammatory processes or areas of increased blood flow.
- Radiation exposure:The radioactive tracer used in the scan involves a small amount of radiation exposure, which should be considered, especially for pregnant women or children.
Compared to alternative imaging techniques, such as CT scans or MRI, a Ceretec white blood cell scan offers a unique perspective on white blood cell activity. While CT and MRI scans provide detailed anatomical images, they do not directly assess white blood cell activity.
Therefore, a Ceretec scan can provide complementary information in certain clinical situations.
Clinical Applications of a Ceretec White Blood Cell Scan
A Ceretec white blood cell scan plays a significant role in clinical practice, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various medical conditions.
Diagnosis of Infections
Ceretec scans are particularly valuable in detecting and localizing infections, especially those involving bones, joints, or soft tissues. By highlighting areas of increased white blood cell activity, the scan can pinpoint the site of infection, enabling targeted treatment.
Treatment Planning and Monitoring
The results of a Ceretec scan can guide treatment decisions by providing information about the severity and extent of an infection. It can help determine the appropriate antibiotic therapy and monitor its effectiveness over time. Serial scans can track the response to treatment, allowing adjustments to be made as necessary.
Monitoring Disease Progression
Ceretec scans are also useful in monitoring the progression of certain diseases, such as osteomyelitis or inflammatory bowel disease. By tracking changes in white blood cell activity over time, the scan can provide insights into disease activity and help predict disease outcomes.
FAQ Summary
What is a Ceretec white blood cell scan used for?
Ceretec scans are used to detect and locate infections and inflammation throughout the body, particularly in the bones and soft tissues.
How is a Ceretec scan performed?
A small amount of radioactive tracer is injected into a vein, which then travels through the bloodstream and accumulates in areas of infection or inflammation. A special camera is then used to take images of the body, revealing the location and extent of the affected areas.
What are the advantages of a Ceretec scan?
Ceretec scans are highly sensitive and specific for detecting infections and inflammation, and they can provide valuable information that may not be available from other imaging tests.
What are the limitations of a Ceretec scan?
Ceretec scans can be expensive, and they may not be suitable for all patients, such as those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.